To achieve centimeter precision Reach RS uses the technology called RTK.
RTK, Real-Time Kinematics
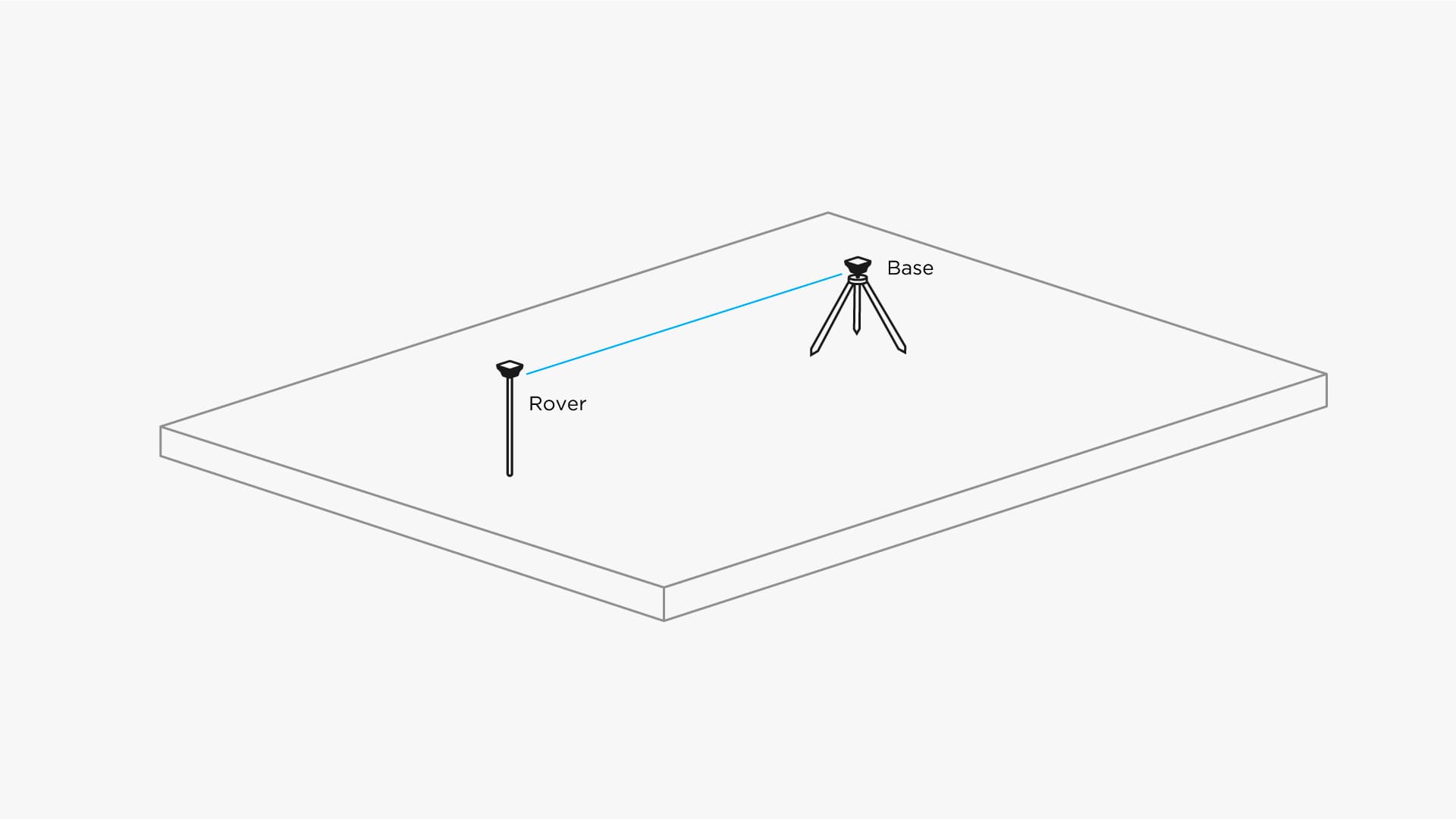
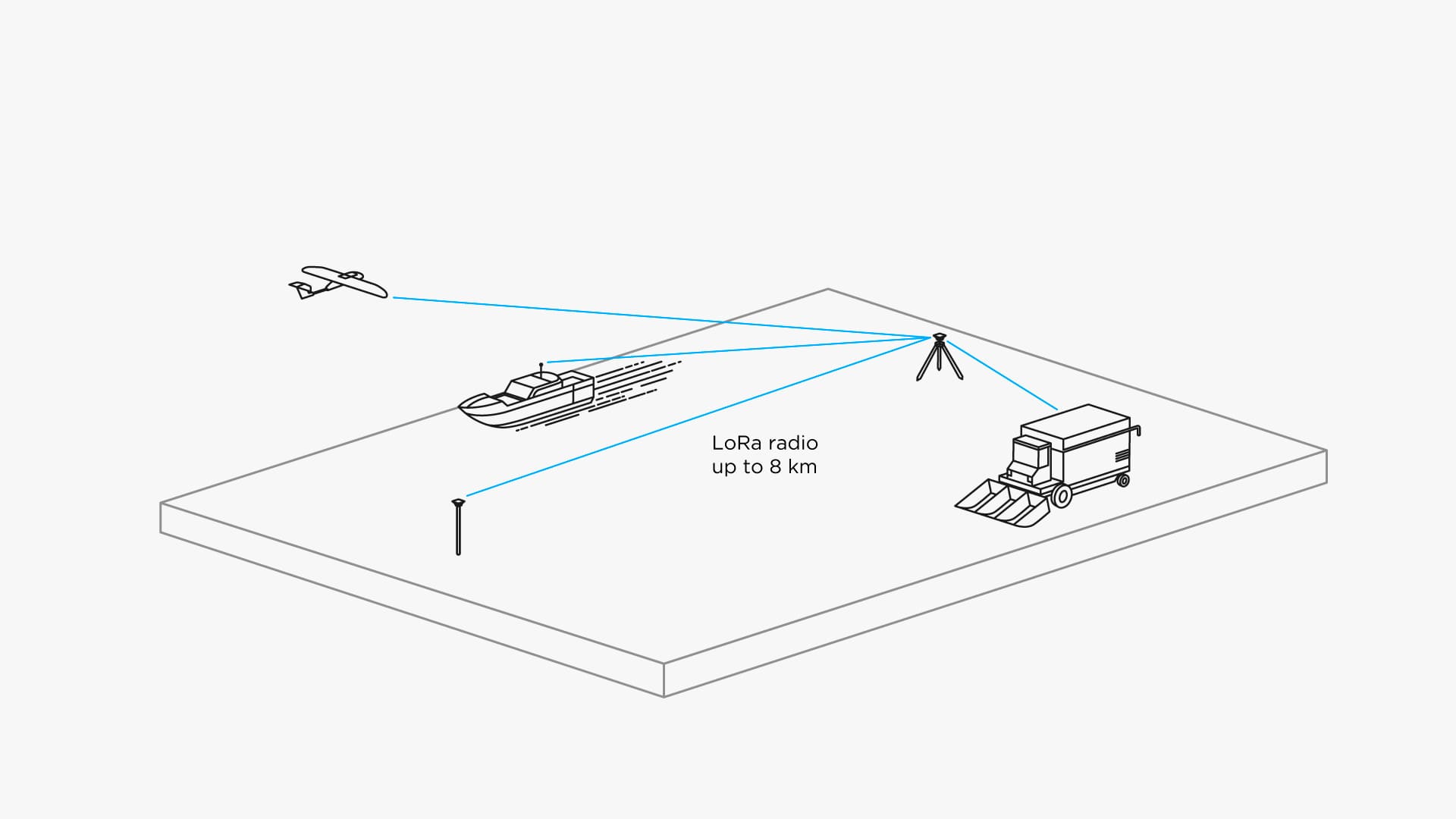
Two Reach RS receivers work together. One is stationary, another moves freely. They’re usually called base and rover. Rover can’t calculate it’s precise position using only satellites signals, it needs a reference, and that’s what base is for. Rover connects to it and calculates relative position with centimeter precision.
They communicate over LoRa radio, which can work on distance up to 8 km. Multiple rovers can be connected to one base at the same time.
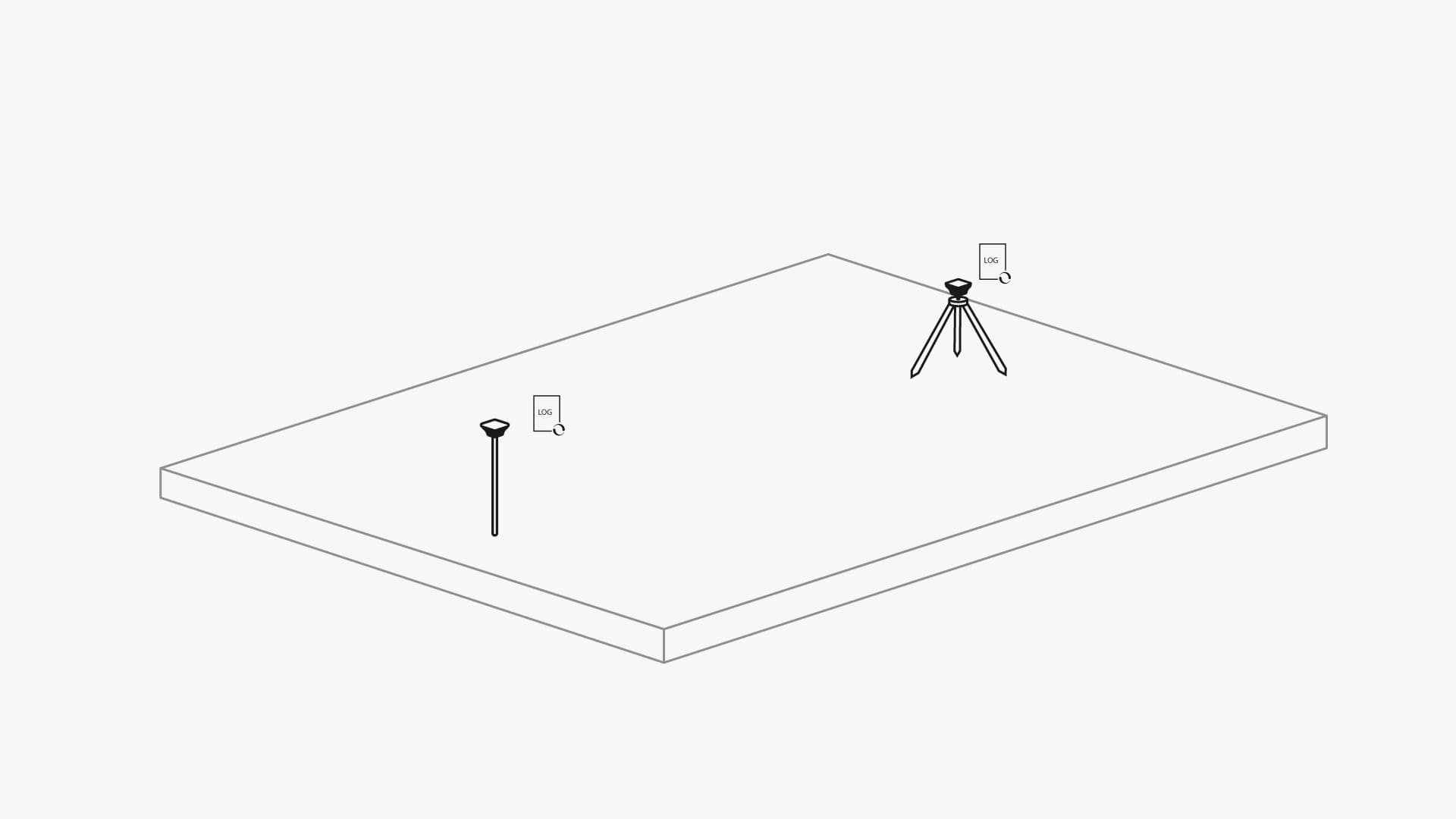
PPK, Post-Processed Kinematics
Along with RTK Reach supports PPK or Post-processed kinematic. This mode doesn’t require real-time connection between base and rover, making equipment setup simpler. In PPK all raw measurement data is recorded on receivers and is processed afterward to get centimeter precision.
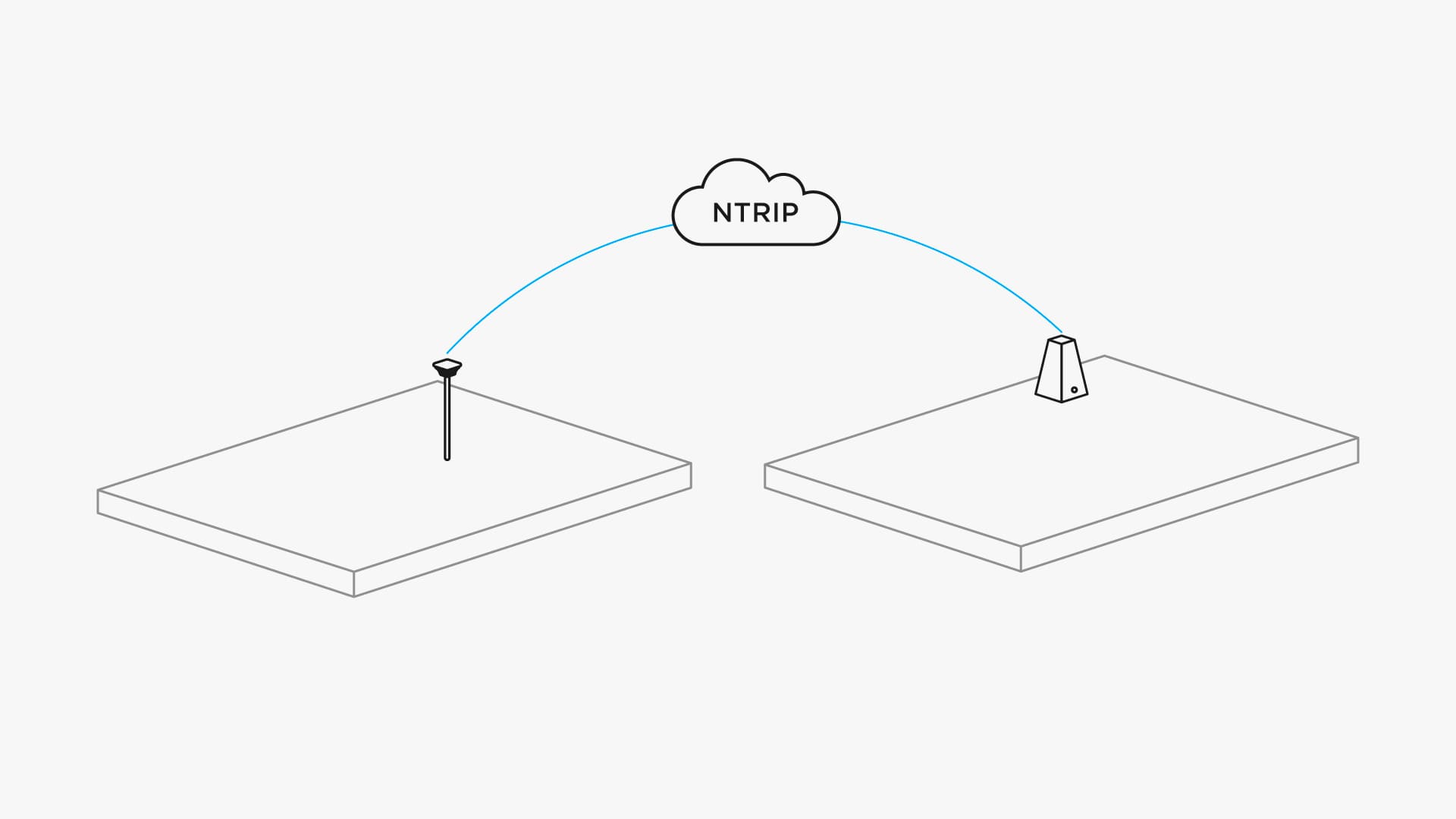
NTRIP
You also don’t necessarily need a second unit for RTK. Usually there are local organizations that share their base stations over the Internet. This technology is called NTRIP. Basically, you just borrow base station from someone in your area. And you can also share your own.
NTRIP is a good option for occasional use and for areas with strong 3G/LTE coverage. In other cases using second Reach RS+ as a local base station has two advantages:
— Autonomy in the remote areas as there’s no need in the Internet connection;
— Independency from local providers, no additional fees by NTRIP service.